gempy.core.solution.Solution¶
-
class
gempy.core.solution.Solution(grid: Optional[gempy.core.data.Grid] = None, surfaces: Optional[gempy.core.data.Surfaces] = None, series: Optional[gempy.core.data_modules.stack.Series] = None)[source]¶ This class stores the output of the interpolation and the necessary objects to visualize and manipulate this data.
- Depending on the activated grid (see
Grid) a different number of properties are returned returned:
- Parameters
grid (Grid) – [s0] Class to generate grids.
surfaces (Surfaces) – [s1] Class that contains the surfaces of the model and the values of each of them.
series (Series) – [s2] Class that contains the functionality and attributes related to the series. Notice that series does not onlyrefers to stratigraphic series but to any set of surfaces which will be interpolated together (comfortably).
-
weights_vector¶ [s3] Numpy array that containing the kriging weights for each input data sorted by series
- Type
numpy.array
-
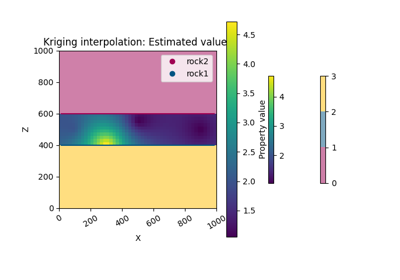
scalar_field_at_surface_points¶ [s4] Value of the scalar field at each interface. Axis 0 is each series and axis 1 contain each surface in orde
- Type
numpy.array
-
block_at_surface_points¶ [s5] 3D array with all interpolated values for a given series and at the interface
- Type
numpy.array
-
mask_at_surface_points¶ [s6] Boolean array containing the logic to combine multiple series to obtain the final model at each interface
- Type
numpy.array
-
values_at_surface_points¶ [s7] 2D array with the final values once the superposition of series has been carried out at each interface
- Type
numpy.array
-
lith_block¶ [s8] Array with the id of each layer evaluated in each point of the regular grid.
- Type
numpy.array
-
scalar_field_matrix¶ [s9] Value of the scalar field at each value of the regular grid.
- Type
numpy.array
-
block_matrix¶ [s10] 3D array with all interpolated values for a given series and at each value of the regular grid.
- Type
numpy.array
-
mask_matrix¶ [s11] Boolean array containing the logic to combine multiple series to obtain the final model at each value of the regular grid.
- Type
numpy.array
-
mask_matrix_pad¶ mask matrix padded 2 block in order to guarantee that the layers intersect each other after marching cubes
- Type
numpy.array
-
values_matrix¶ [s12] 2D array with the final values once the superposition of series has been carried out at each value of the regular grid
- Type
numpy.array
-
vertices¶ [s13] List of numpy arrays containing the XYZ coordinates of each triangle vertex
- Type
list[numpy.array]
-
edges¶ [s14] List of numpy arrays containing the indices of the vertices numpy arrays that compose each individual triangle.
- Type
list[numpy.array]
-
geological_map¶ [s15] 2D array containing the lithologies at the surfaces.
- Type
numpy.array
Examples using Solution
Methods
__init__([grid, surfaces, series])Initialize self.
add_cartesian_coords(coords_base)compute_all_surfaces(**kwargs)Compute all surfaces of the model given the geological features rules.
compute_marching_cubes_regular_grid(level, …)Compute the surface (vertices and edges) of a given surface by computing
create_struc_xarrays(values, l0, l1, res)create_unstruct_xarray(values, l0, l1, xyz)extract_each_surface_representations(ids, …)padding_mask_matrix([mask_topography, shift])Pad as many elements as in shift to the masking arrays. This is done
prepare_common_args(active_features, …)prepare_marching_cubes_args(e, …)set_meshes([surfaces])Create xarray from the Surfaces object.
set_solution_to_custom(values)set_solution_to_regular_grid(values[, …])If regular grid is active set all the solution objects dependent on them and compute mesh.
set_solution_to_sections(values)set_solution_to_topography(values)set_solutions(sol, compute_mesh, sort_surfaces)set_values(values[, active_features, …])At this stage we should split values into the different grids
set_values_to_centered()set_values_to_custom_grid(values, l0, l1, …)set_values_to_regular_grid(values)Set all solution values to the correspondent attribute.
set_values_to_regular_grid_(values, l0, l1, …)set_values_to_sections(values, l0, l1, …)set_values_to_surface_points(values)set_values_to_surface_points_(values, l0, …)set_values_to_topography(values, l0, l1, …)set_vertices_edges(active_indices, s, s_n, v)to_netcdf(path, name, **kwargs)try_compute_marching_cubes_on_the_regular_grid(…)Attributes
data_structures-
__init__(grid: Optional[gempy.core.data.Grid] = None, surfaces: Optional[gempy.core.data.Surfaces] = None, series: Optional[gempy.core.data_modules.stack.Series] = None)[source]¶ Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
-
set_solution_to_regular_grid(values: Union[list, numpy.ndarray], compute_mesh: bool = True, compute_mesh_options: Optional[dict] = None)[source]¶ If regular grid is active set all the solution objects dependent on them and compute mesh.
- Parameters
values (list[np.array]) –
list with result of the theano evaluation (values returned by
gempy.compute_model()function):block_matrix
weights_vector
scalar_field_matrix
scalar field at interfaces
mask_matrix
compute_mesh (bool) – if True perform marching cubes algorithm to recover the surface mesh from the implicit model.
compute_mesh_options (dict) – options for the marching cube function. - rescale: True
- Returns
gempy.core.solutions.Solutions
-
set_values_to_regular_grid(values: Union[list, numpy.ndarray])[source]¶ Set all solution values to the correspondent attribute.
- Parameters
values (np.ndarray) – values returned by function: gempy.compute_model function
compute_mesh (bool) – if true compute automatically the grid
- Returns
gempy.core.solutions.Solutions
-
compute_marching_cubes_regular_grid(level: float, scalar_field, mask_array=None, rescale=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ - Compute the surface (vertices and edges) of a given surface by computing
marching cubes (by skimage)
- Parameters
level (float) – value of the scalar field at the surface
scalar_field (np.array) – scalar_field vector objects
mask_array (np.array) – mask vector with trues where marching cubes has to be performed
rescale (bool) – if True surfaces will be located between 0 and 1
**kwargs – skimage.measure.marching_cubes_lewiner args (see below)
- Returns
vertices, simplices, normals, values
- Return type
See also
-
padding_mask_matrix(mask_topography=True, shift=2)[source]¶ - Pad as many elements as in shift to the masking arrays. This is done
to guarantee intersection of layers if masked marching cubes are done
- Parameters
mask_topography (bool) – if True mask also the topography. Default True
shift – Number of voxels shifted for the topology. Default 1.
- Returns
masked regular grid
- Return type
-
compute_all_surfaces(**kwargs)[source]¶ Compute all surfaces of the model given the geological features rules.
- Parameters
**kwargs –
skimage.measure.marching_cubesargs (see below)- Returns
vertices and edges
- Return type
- Depending on the activated grid (see