Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Video Tutorial “code-along”: Modeling step by step¶
This tutorial demonstrates step-by-step geological modeling using the gempy and gempy_viewer libraries. It follows the Video tutorial series available on the gempy YouTube channel.
Video tutorial 1: Introduction¶
The first video is an introduction to GemPy - please view online before starting the tutorial.
Video tutorial 2: Input data¶
# Required imports
import gempy as gp
import gempy_viewer as gpv
# Path to input data
data_path = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cgre-aachen/gempy_data/master/"
path_to_data = data_path + "/data/input_data/video_tutorials_v3/"
# Create instance of geomodel
geo_model = gp.create_geomodel(
project_name = 'tutorial_model',
extent=[0,2500,0,1000,0,1000],
resolution=[100,40,40],
importer_helper=gp.data.ImporterHelper(
path_to_orientations=path_to_data+"tutorial_model_orientations.csv",
path_to_surface_points=path_to_data+"tutorial_model_surface_points.csv"
)
)
Surface points hash: 7c6d3e04ab03a4b8324d9c91d56c30f9e6a7cb6c22c6f2ee69a5dd001c63337a
Orientations hash: 63e42d294dec66b4db2f175bc7b58553ee89d68f3072d36402963c90b0ef5262
# Display a basic cross section of input data
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model)
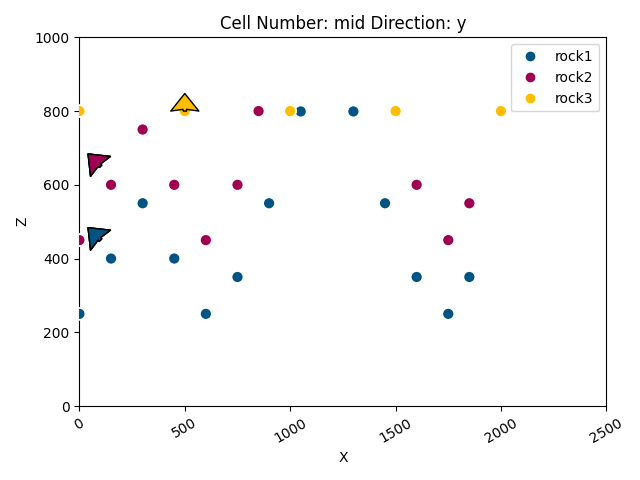
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff253785f90>
# Manually add a surface point
gp.add_surface_points(
geo_model=geo_model,
x=[2250],
y=[500],
z=[750],
elements_names=['rock1']
)
# Show added point in cross section
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model)
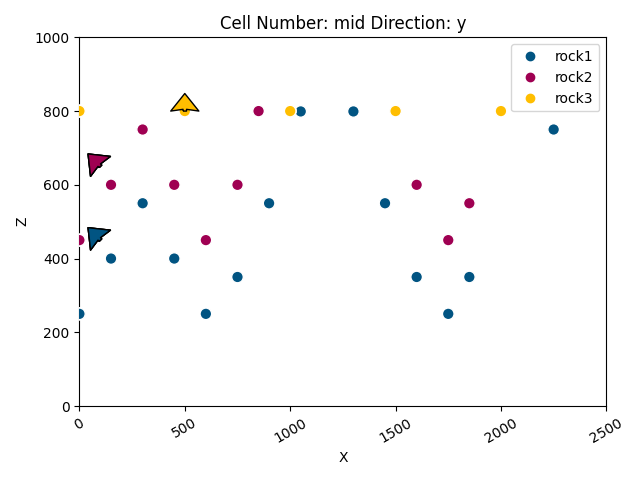
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff253787490>
Video tutorial 3: Structural frame¶
# View structural frame
geo_model.structural_frame
# View structural elements
geo_model.structural_frame.structural_elements
[Element(
name=rock1,
color=#015482,
is_active=True
), Element(
name=rock2,
color=#9f0052,
is_active=True
), Element(
name=rock3,
color=#ffbe00,
is_active=True
), Element(
name=basement,
color=#728f02,
is_active=True
)]
# Define structural groups and age/stratigraphic relationship
gp.map_stack_to_surfaces(
gempy_model=geo_model,
mapping_object={
"Strat_Series2": ("rock3"),
"Strat_Series1": ("rock2", "rock1")
}
)
Video tutorial 4: Computation and results¶
# View interpolation options
geo_model.interpolation_options
InterpolationOptions(kernel_options=KernelOptions(range=1.7, c_o=10.0, uni_degree=1, i_res=4.0, gi_res=2.0, number_dimensions=3, kernel_function=AvailableKernelFunctions.cubic, kernel_solver=Solvers.DEFAULT, compute_condition_number=False, optimizing_condition_number=False, condition_number=None), evaluation_options=EvaluationOptions(_number_octree_levels=1, _number_octree_levels_surface=4, octree_curvature_threshold=-1.0, octree_error_threshold=1.0, octree_min_level=2, mesh_extraction=True, mesh_extraction_masking_options=<MeshExtractionMaskingOptions.INTERSECT: 3>, mesh_extraction_fancy=True, evaluation_chunk_size=500000, compute_scalar_gradient=False, verbose=False), debug=True, cache_mode=<CacheMode.IN_MEMORY_CACHE: 3>, cache_model_name='tutorial_model', block_solutions_type=<BlockSolutionType.DENSE_GRID: 2>, sigmoid_slope=5000000, debug_water_tight=False, temp_interpolation_values=TempInterpolationValues(current_octree_level=0))
# Compute a solution for the model
gp.compute_model(geo_model)
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.numpy
Chunking done: 7 chunks
Chunking done: 30 chunks
# Display the result in 2d section
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, cell_number=20)
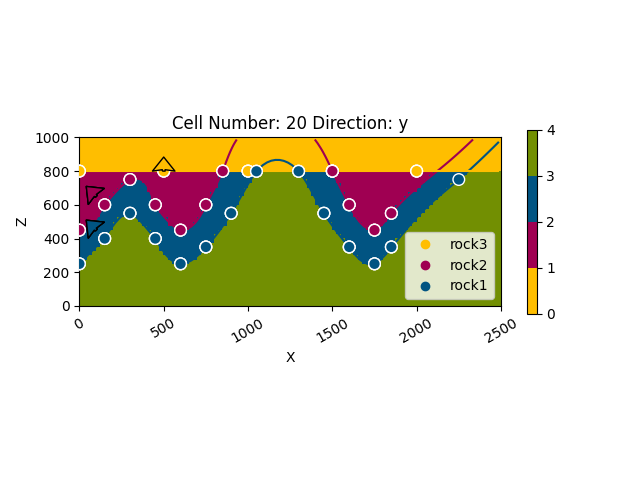
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff2a5527e20>
# Some examples of how to access results
print(geo_model.solutions.raw_arrays.lith_block)
print(geo_model.grid.dense_grid.values)
[4 4 4 ... 1 1 1]
[[ 12.5 12.5 12.5]
[ 12.5 12.5 37.5]
[ 12.5 12.5 62.5]
...
[2487.5 987.5 937.5]
[2487.5 987.5 962.5]
[2487.5 987.5 987.5]]
Video tutorial 5: 2D visualization¶
# 2d plotting options
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, show_value=True, show_lith=False, show_scalar=True, series_n=1, cell_number=25)
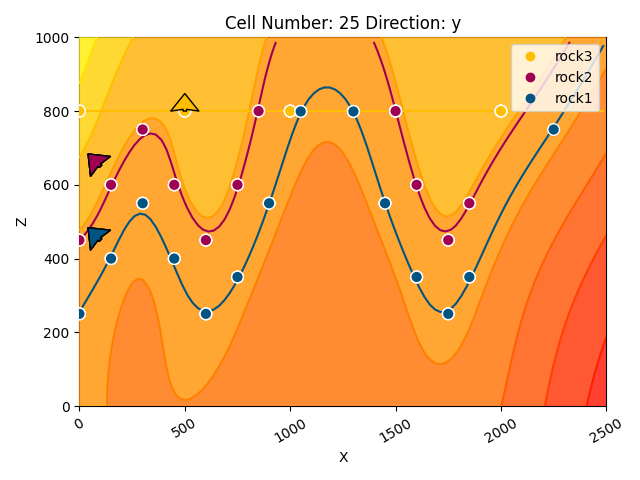
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff24ed0a4d0>
# Create custom section lines
gp.set_section_grid(
grid=geo_model.grid,
section_dict={
'section1': ([0, 0], [2500, 1000], [100, 50]),
'section2': ([1000, 1000], [1500, 0], [100, 100]),
}
)
Active grids: GridTypes.NONE|SECTIONS|DENSE
# Show custom cross-section traces
gpv.plot_section_traces(geo_model)
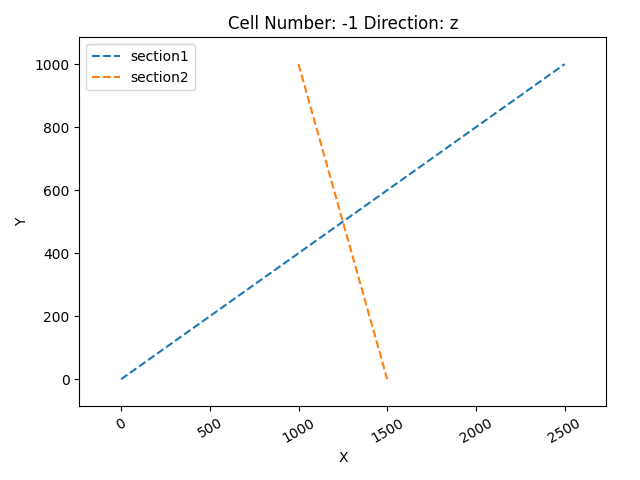
<function plot_section_traces at 0x7ff2ac8252d0>
# Recompute model as a new grid was added
gp.compute_model(geo_model)
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.numpy
Chunking done: 8 chunks
Chunking done: 33 chunks
# Display custom cross-sections
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, section_names=['section1', 'section2'], show_data=False)
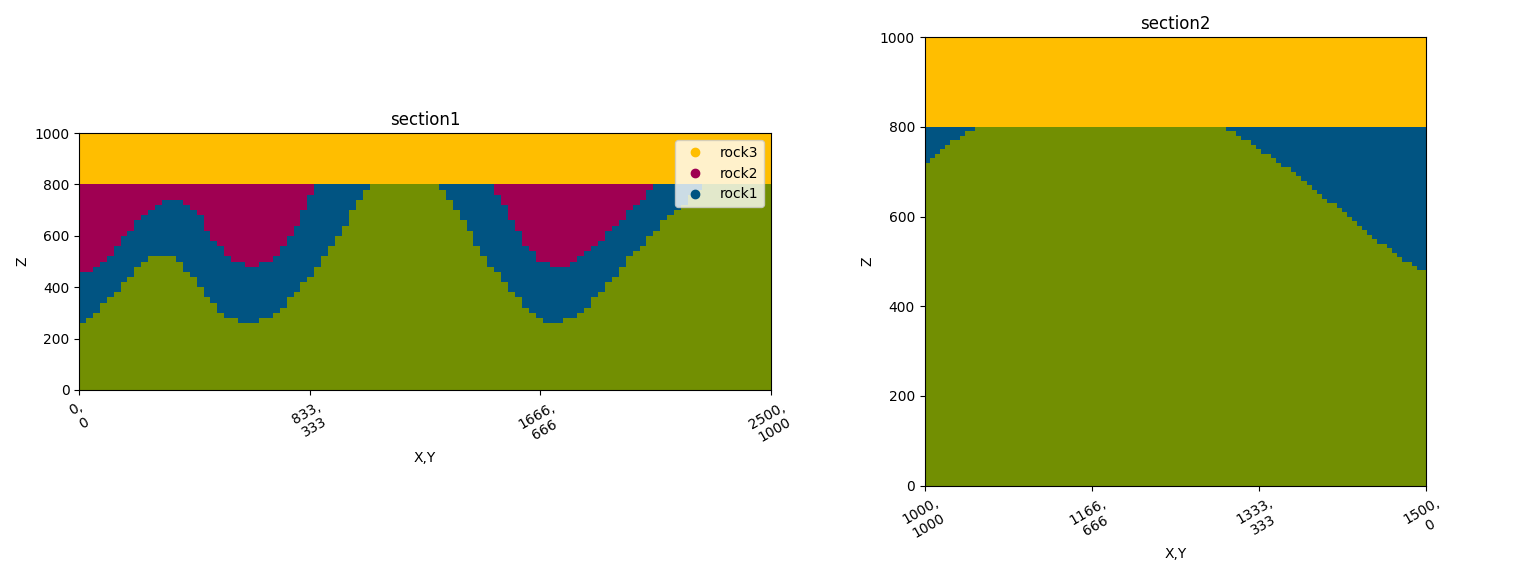
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff2a2a50f10>
Video tutorial 6: 3D visualization¶
# Display the result in 3d
gpv.plot_3d(geo_model, show_lith=True, show_boundaries=True, ve=None)
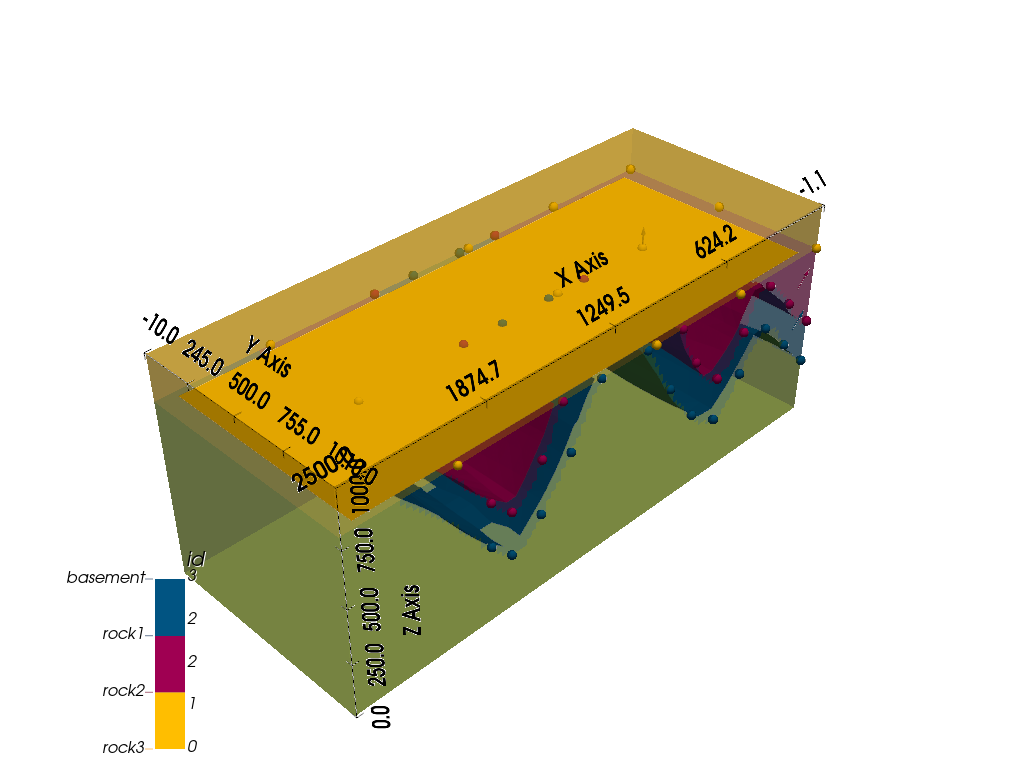
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_3d.vista.GemPyToVista object at 0x7ff2a2bbe200>
# How to access DC meshes
geo_model.solutions.dc_meshes[0].dc_data
# transform mesh vertices to original coordinate system
back_transformed_vertices = geo_model.input_transform.apply_inverse(geo_model.solutions.dc_meshes[0].vertices)
Video tutorial 7: Topography¶
# Setting a randomly generated topography
import numpy as np
gp.set_topography_from_random(
grid=geo_model.grid,
fractal_dimension=1.2,
d_z=np.array([700, 900]),
topography_resolution=np.array([250, 100])
)
Active grids: GridTypes.NONE|SECTIONS|TOPOGRAPHY|DENSE
<gempy.core.data.grid_modules.topography.Topography object at 0x7ff24e9931c0>
# Recompute model as a new grid was added
gp.compute_model(geo_model)
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.numpy
Chunking done: 9 chunks
Chunking done: 37 chunks
# Display a cross-section with topography
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, show_topography=True)
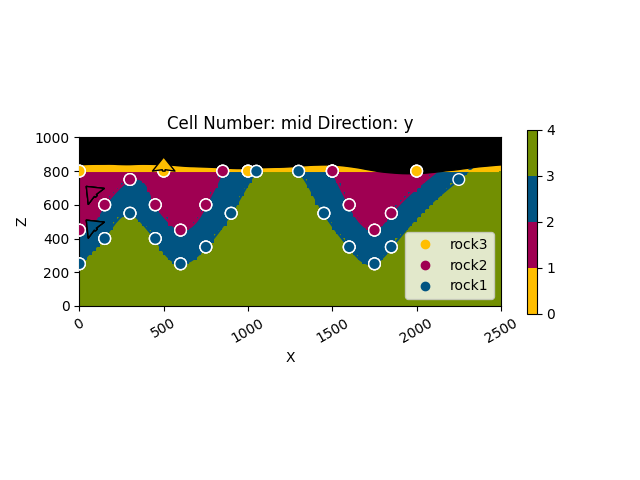
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff24efe5930>
# Displaying a geological map
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, show_topography=True, section_names=['topography'], show_boundaries=False, show_data=False)
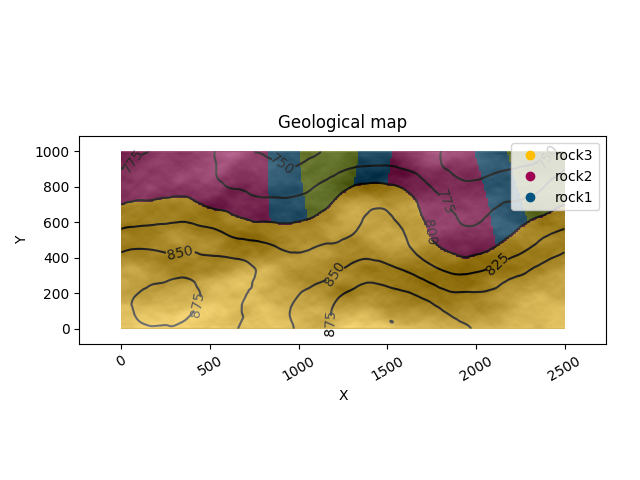
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7ff2a2b2a9b0>
# Display the 3d model with topography
gpv.plot_3d(geo_model, show_lith=True, show_topography=True)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = -1
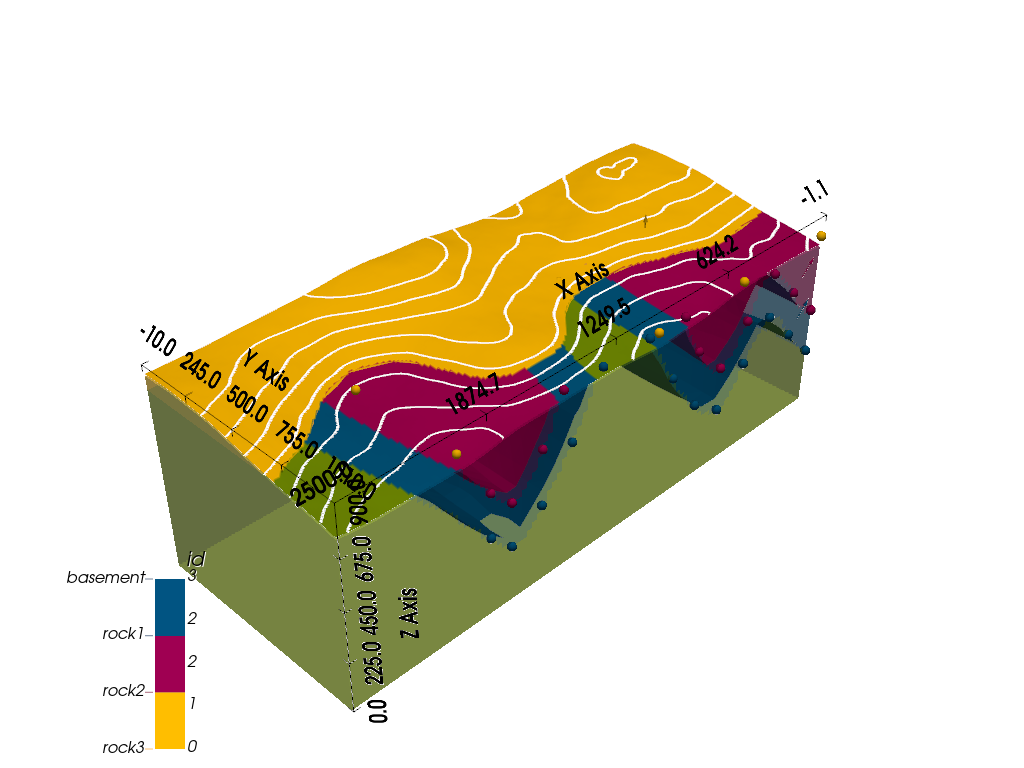
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_3d.vista.GemPyToVista object at 0x7ff2a5f28220>
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 27.717 seconds)
